기본적인 프로젝트를 생성하면 다음과 같은 web.xml이 생성되어 있을 것이다.
기본적으로 "/"경로를 호출할 때, 쓰일 수 있는 페이지의 형식을 <welcome-file>로 정의해 놓았다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>servlettest</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
앱을 외부로 디플로이 하기 위해 자신의 프로젝트를 톰캣에 추가 하였을 것이다.
web.xml에 매핑을 하지 않았을 경우, Servlet을 호출 할 때
http://<YOUR_IP_ADDRESS>/<ROOT_CONTEXT>/<패키지 이름이 포함된 클래스 이름>과 같이 매우 긴 주소로 호출 할 것이다.
하지만 이러한 형식은 클래스 이름이 그대로 노출되기 때문에 보안상 좋지 않습니다. 따라서 이런 방식으로 사용하지 않고, 서블릿 클래스에 대해 대응하는 매핑된 이름으로 실제 서블릿을 요청한다.
매핑을 web.xml에서 정의 할 수 있는데 정의하는 방식은 다음과 같다.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mappingname</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>package.YourServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mappingname</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/name</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
1. <servlet> 태그
이 태그는 프로젝트 내부의 servlet를 외부에 드러낼 수 있도록 servlet에 이름을 지어주는 역할을 한다.
<servlet-name>태그를 이용하여 서블릿의 이름을 지어주고,
<servlet-class>태그를 이용하여 이름을 지어 줄 서블릿을 선언한다.
2. <servlet-mapping> 태그
이 태그는 내부의 servlet와 외부 요청에 대한 논리적인 경로를 설정해준다.
<servlet-name>태그를 이용하여 외부에 드러낼 서블릿의 이름을 설정한 다음,
<url-pattern>태그를 이용하여 외부에서 접근할 url 경로를 설정해준다.
위를 테스트 하기 위해 나는 test패키지를 생성하여 testServlet 클래스를 생성하였다.
package test;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class testServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("doGet method is called");
super.doGet(req, resp);
} // get 요청에 대한 override class이며, get방식에 대해 요청을 처리하는 클래스이다.
@Override
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy method is called");
super.destroy();
} // servlet이 종료될 때 호출되는 class
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
System.out.println("init method is called");
super.init();
} //최초 servlet call을 다루는 override class
}
이 Servlet 클래스를 논리적인 주소로 매핑시키기 위해 다음과 같이 web.xml을 수정하였다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>servlettest</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mappingname</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>test.testServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mappingname</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/name</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>mappingname이라는 이름으로 test 패키지의 testServlet클래스에 대해 이름을 지어준 뒤,
"/name" 이라는 논리적인 경로와 매핑시켜주었다.
다음은 테스트 결과 캡쳐 화면이다.

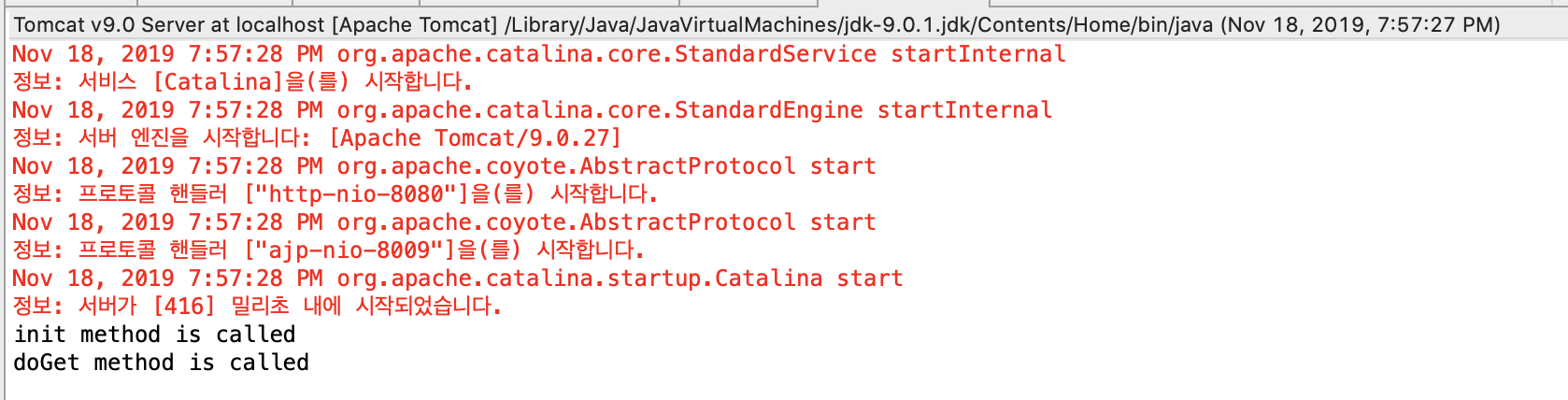
위와 같이 잘 호출 되었음을 알 수 있다.
'IT > Java Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 순차적 프로세스의 비동기식 프로세스로의 전환 삽질 (0) | 2020.10.14 |
|---|---|
| [HikariCP] Possibly consider using a shorter maxLifetime value (0) | 2020.08.12 |
| [Spring] Factory Design Pattern (0) | 2020.08.06 |
| [Spring] @RestController vs @Controller (0) | 2020.02.07 |
| [Spring] Servlet의 동작 과정과 메모리 적재 (0) | 2019.11.19 |